如何在数据库中存储层次结构
常见场景
- 公司:公司 - 部门 - 子部门
- 人员:领导 - 员工
- 文件:根目录 - 文件夹 - 文件
- 关系:group - child
实例
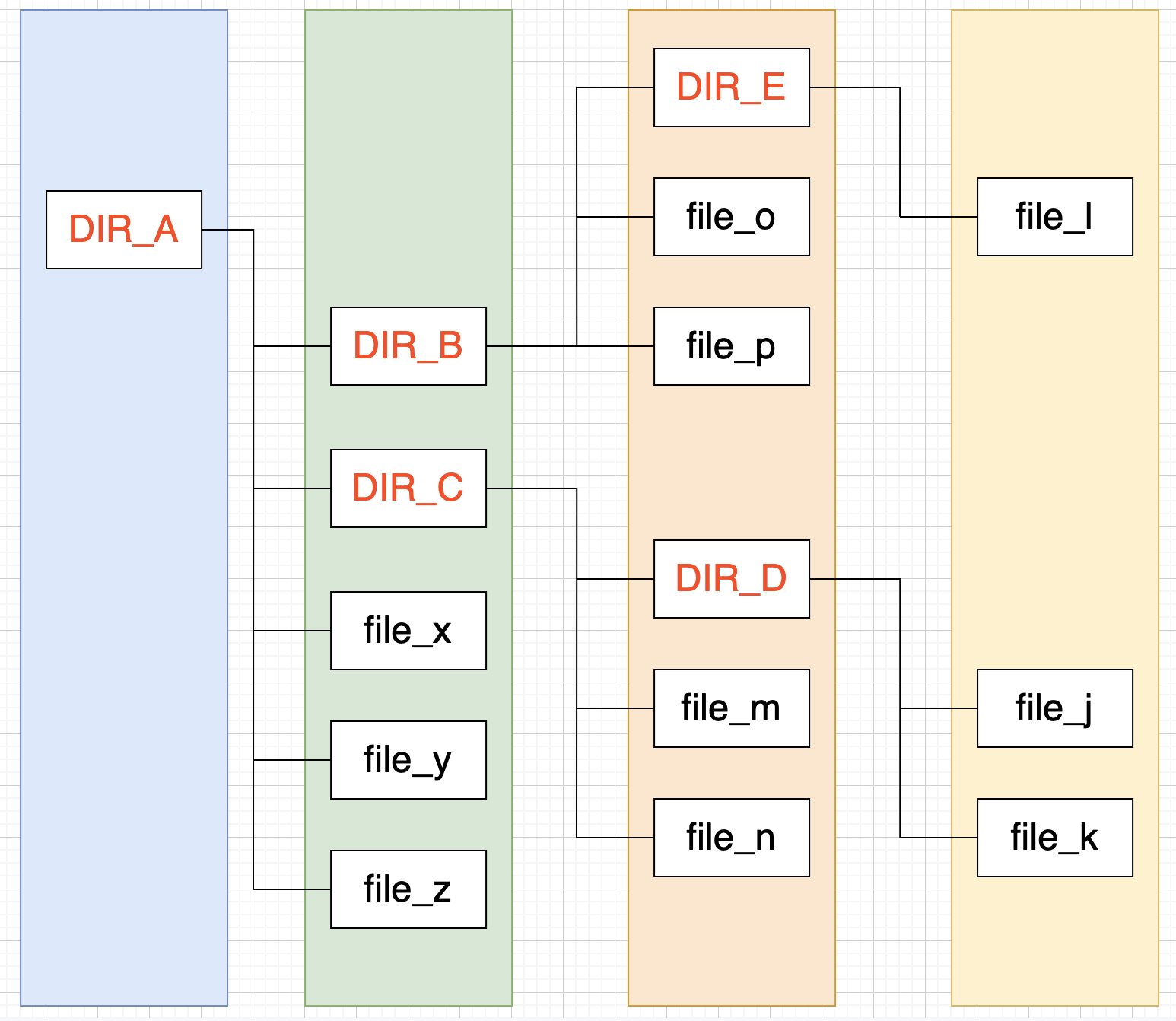
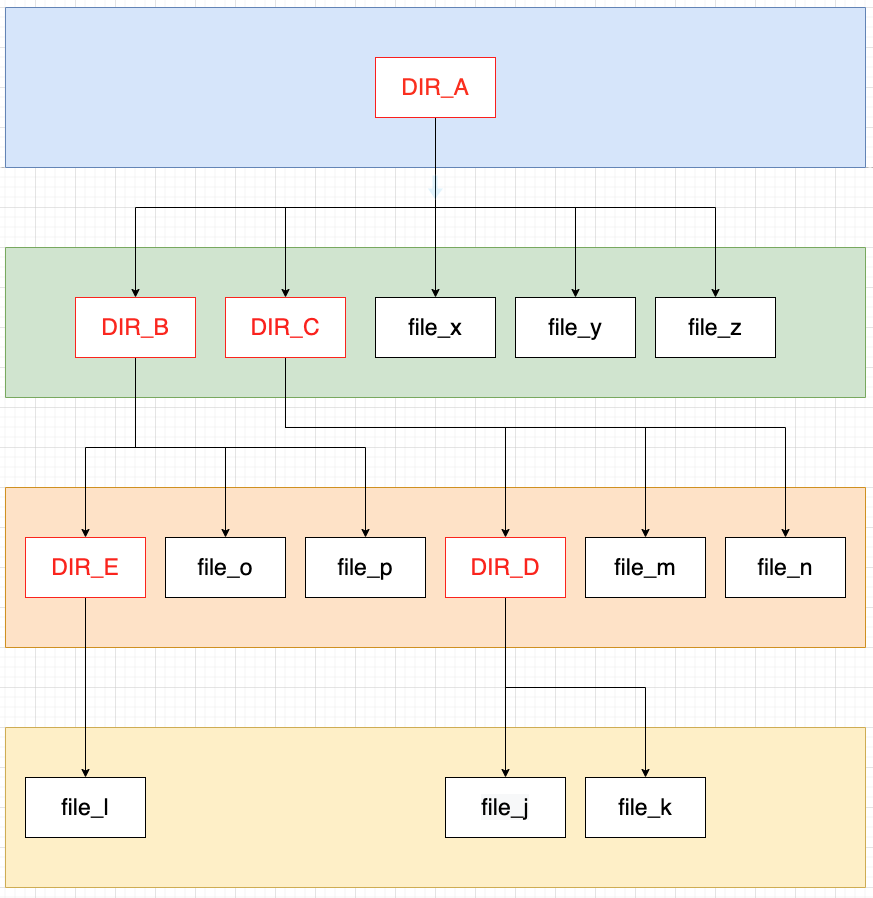
转成树型
Adjacency List 邻接表
存储当前节点的父节点信息(parent_id),通过 parent_id 相关联
| id | name | parent_id |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | DIR_A | root |
| 2 | DIR_B | 1 |
| 3 | DIR_C | 1 |
| 4 | file_x | 1 |
| 5 | file_y | 1 |
| 6 | file_z | 1 |
| 7 | DIR_E | 2 |
| 8 | file_o | 2 |
| 9 | file_p | 2 |
| 10 | DIR_D | 3 |
| 11 | file_m | 3 |
| 12 | file_n | 3 |
| 13 | file_l | 7 |
| 14 | file_j | 10 |
| 15 | file_k | 10 |
各种情况的处理代价
| |
增
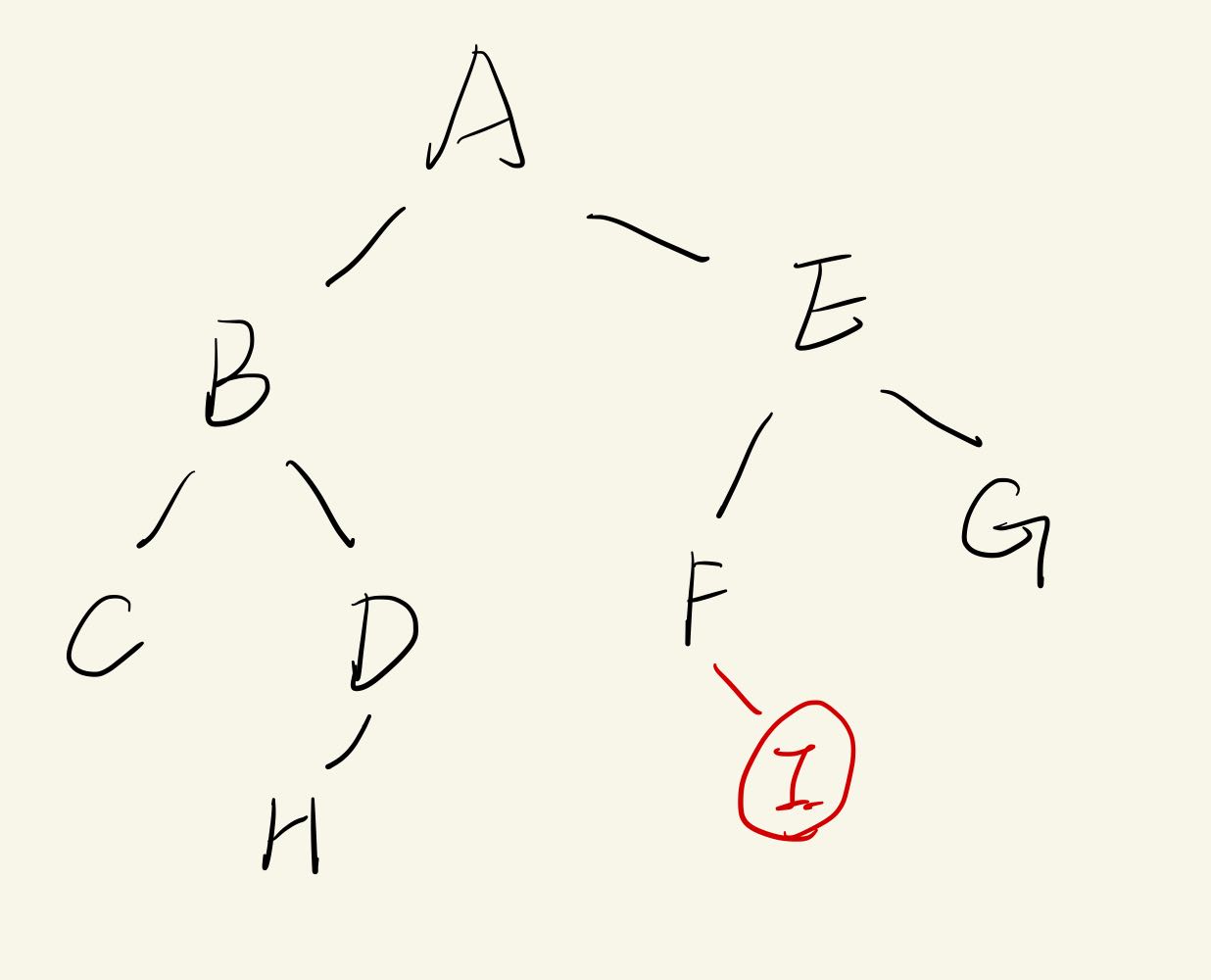
代价:-> O(1)
输入:name, parent_id
执行:
| |
| id | name | parent_id |
|---|---|---|
| 13 | file_l | 7 |
| 14 | file_j | 10 |
| 15 | file_k | 10 |
| 16(add) | file_ADD | 1 |
删
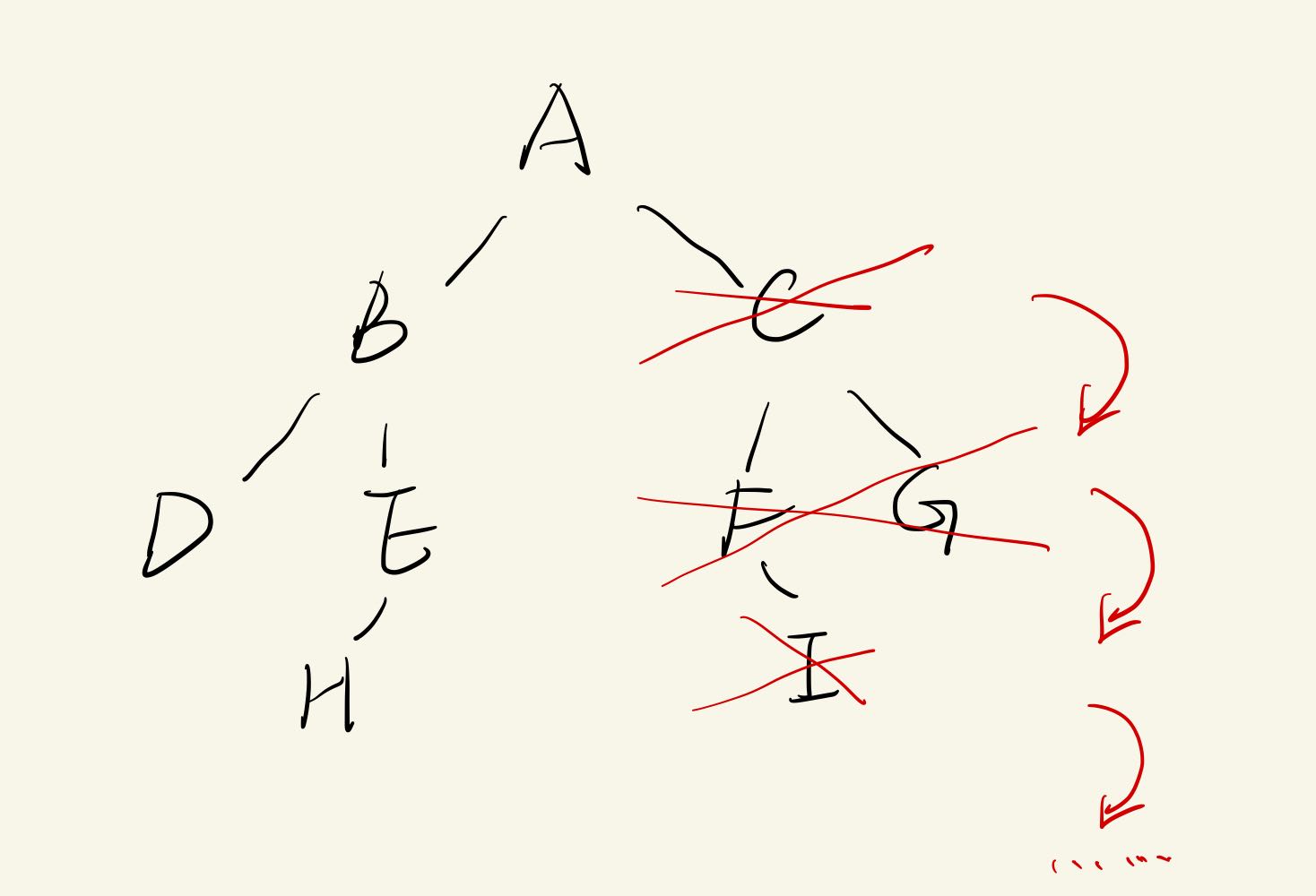
需要递归删除
代价:-> ∞
输入:id
递归执行:
| |
当然也可以只删除直接下级,但会留下“悬浮节点”
改
代价:-> O(1)
输入:id, other info
执行:
| |
查
查自己
代价:-> O(1)
输入:id
执行:
| |
查下一级
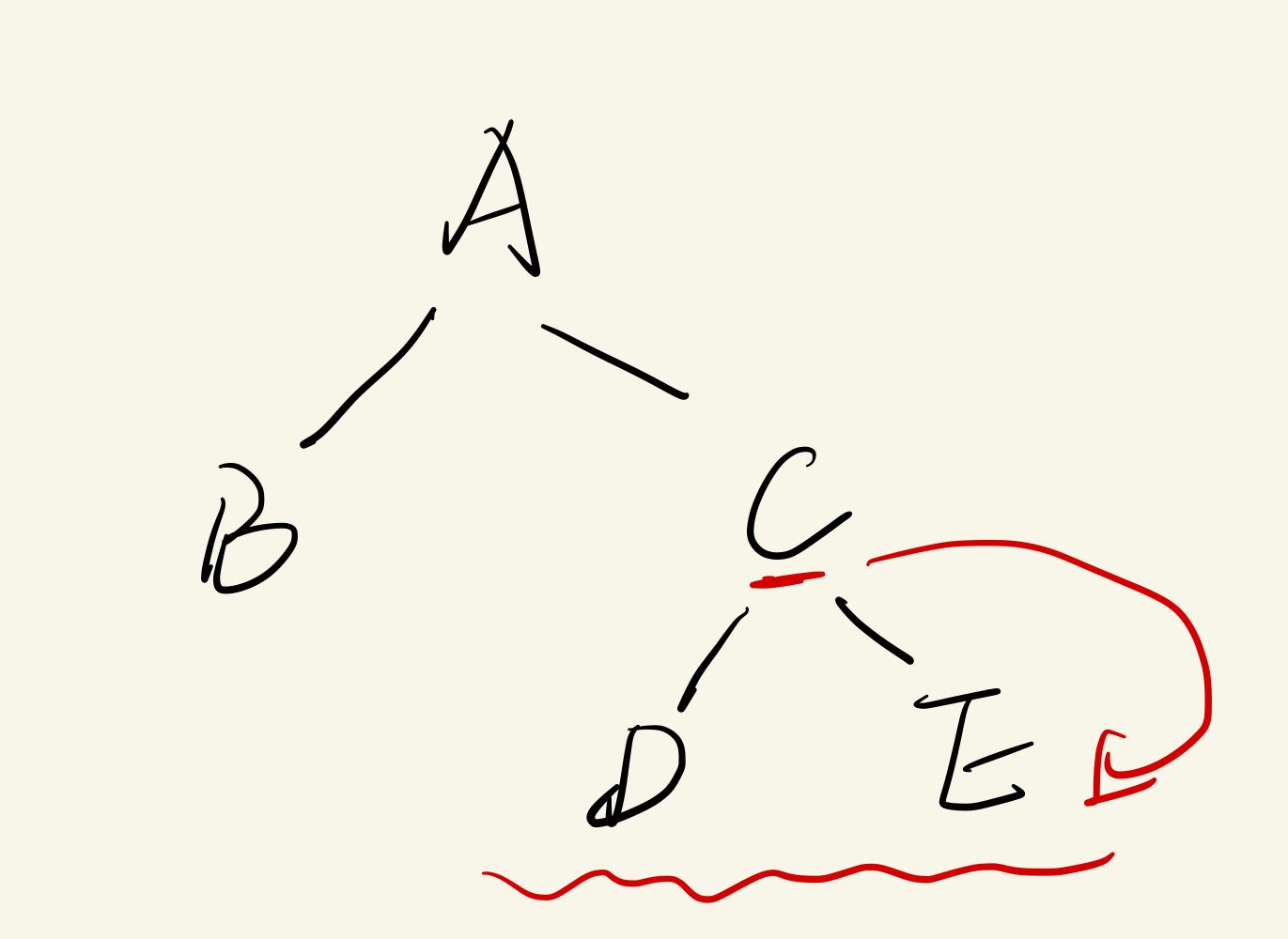
代价:-> O(n)
输入:id
执行:
| |
查所有子集
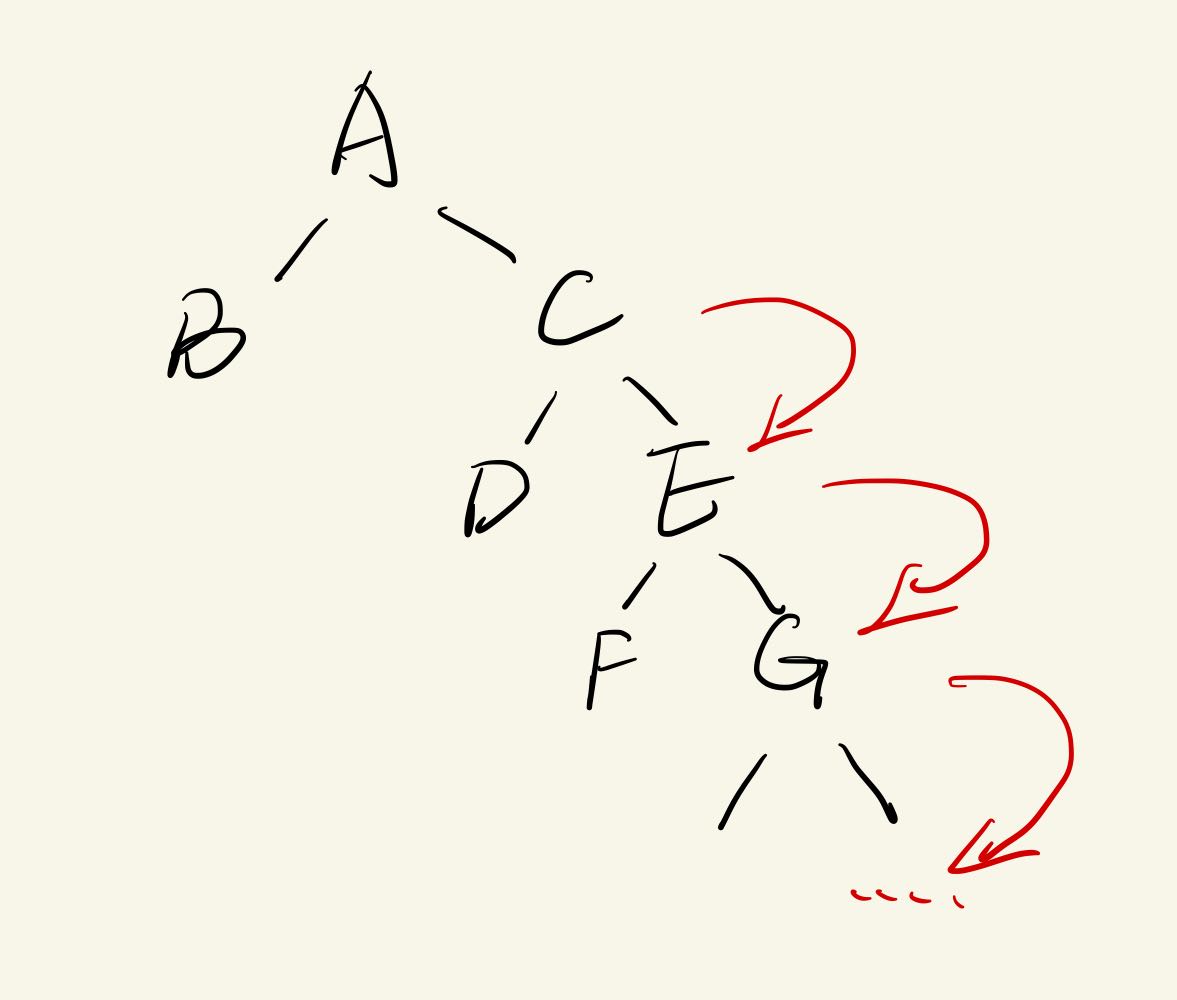
代价:-> ∞
输入:id
执行:
| |
移动
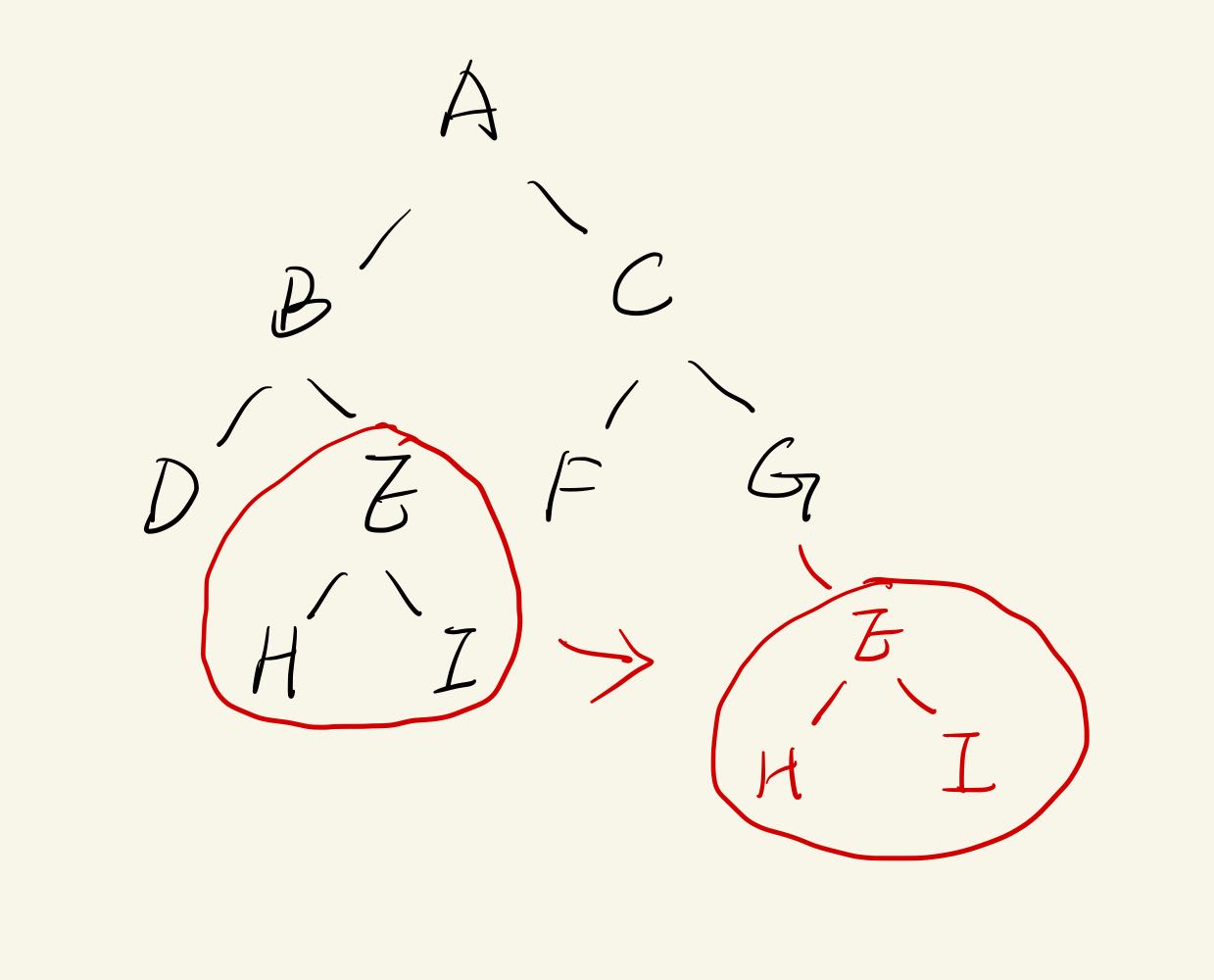
代价:-> O(1)
输入:id, new_parent_id
执行:
| |
总结
优点 : 进行增加、修改、移动时代价很低; 查询自己、直接下级非常方便
缺点 : 如若需要使用层级结构,例如获取所有子目录,所有下级,代价趋近∞(致命)
适用 : 不涉及“所有子集”,严格按照层级一层层地查询