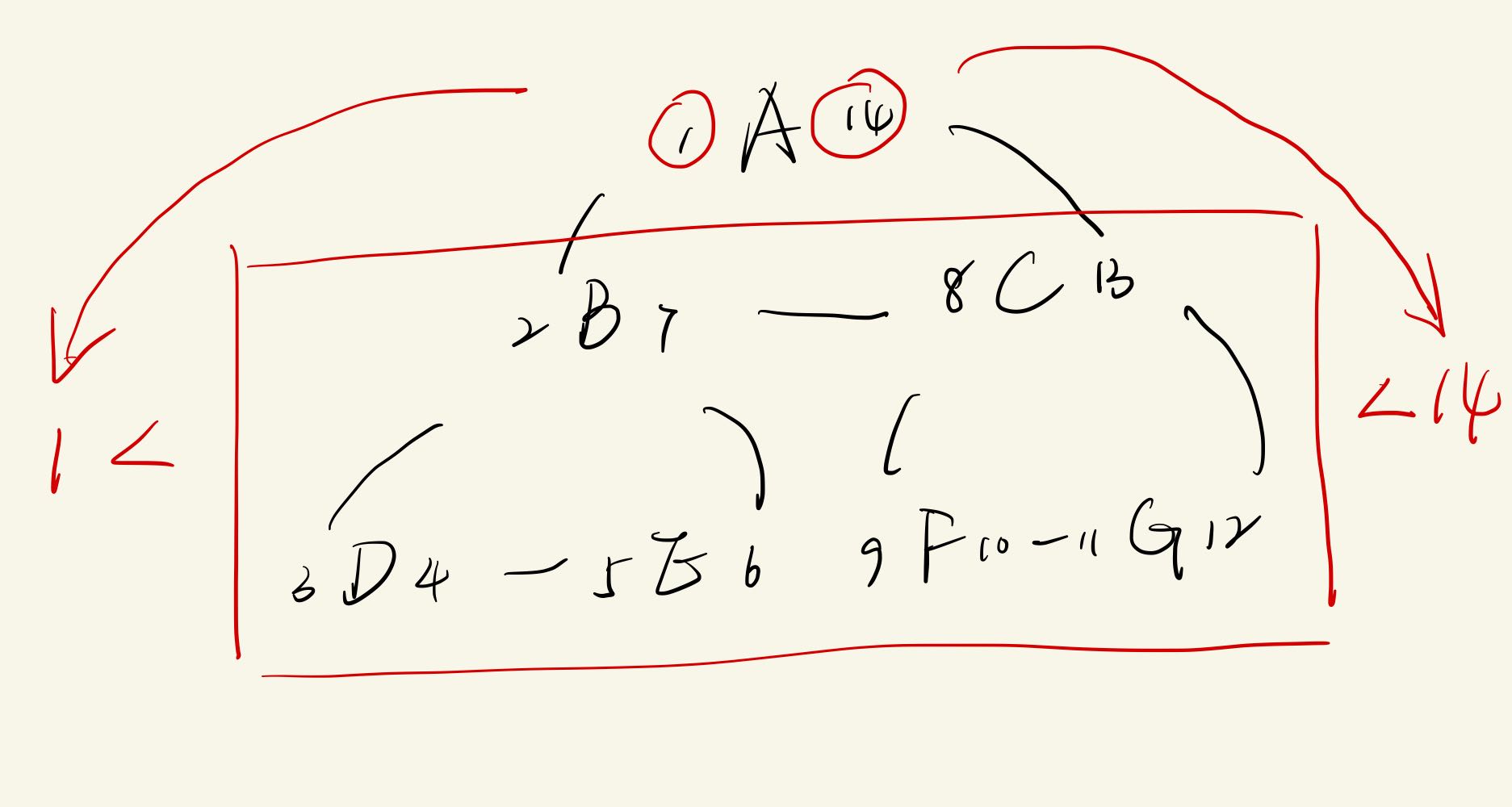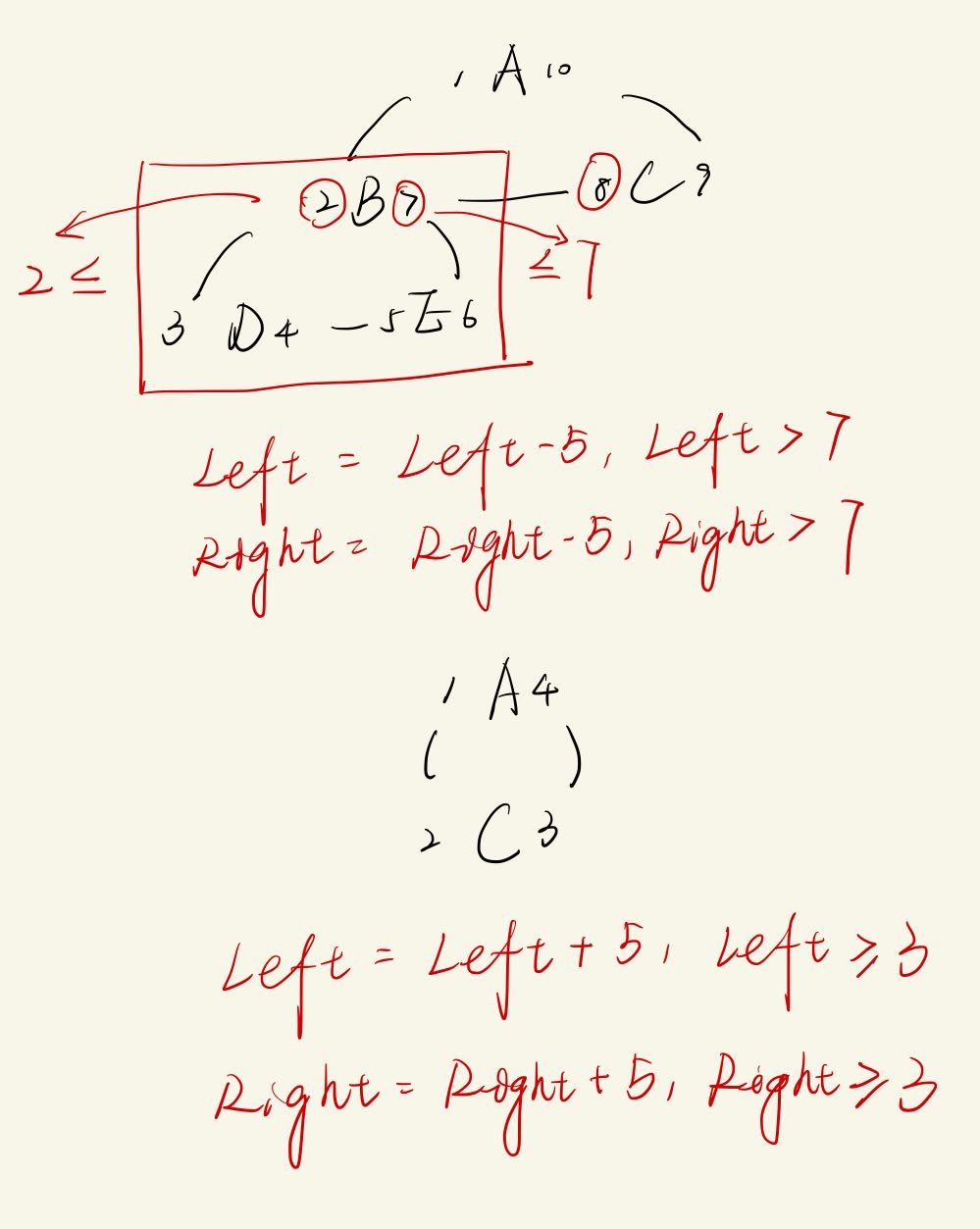如何在数据库中存储层次结构
常见场景
公司:公司 - 部门 - 子部门
人员:领导 - 员工
文件:根目录 - 文件夹 - 文件
关系:group - child
实例
转成树型
回头看
之前提到的几种方案(Adjacency_List, Path_Enumerations, Closure_Table)都能够一定程度地满足需求,但是各自具有不可避免的弊端。
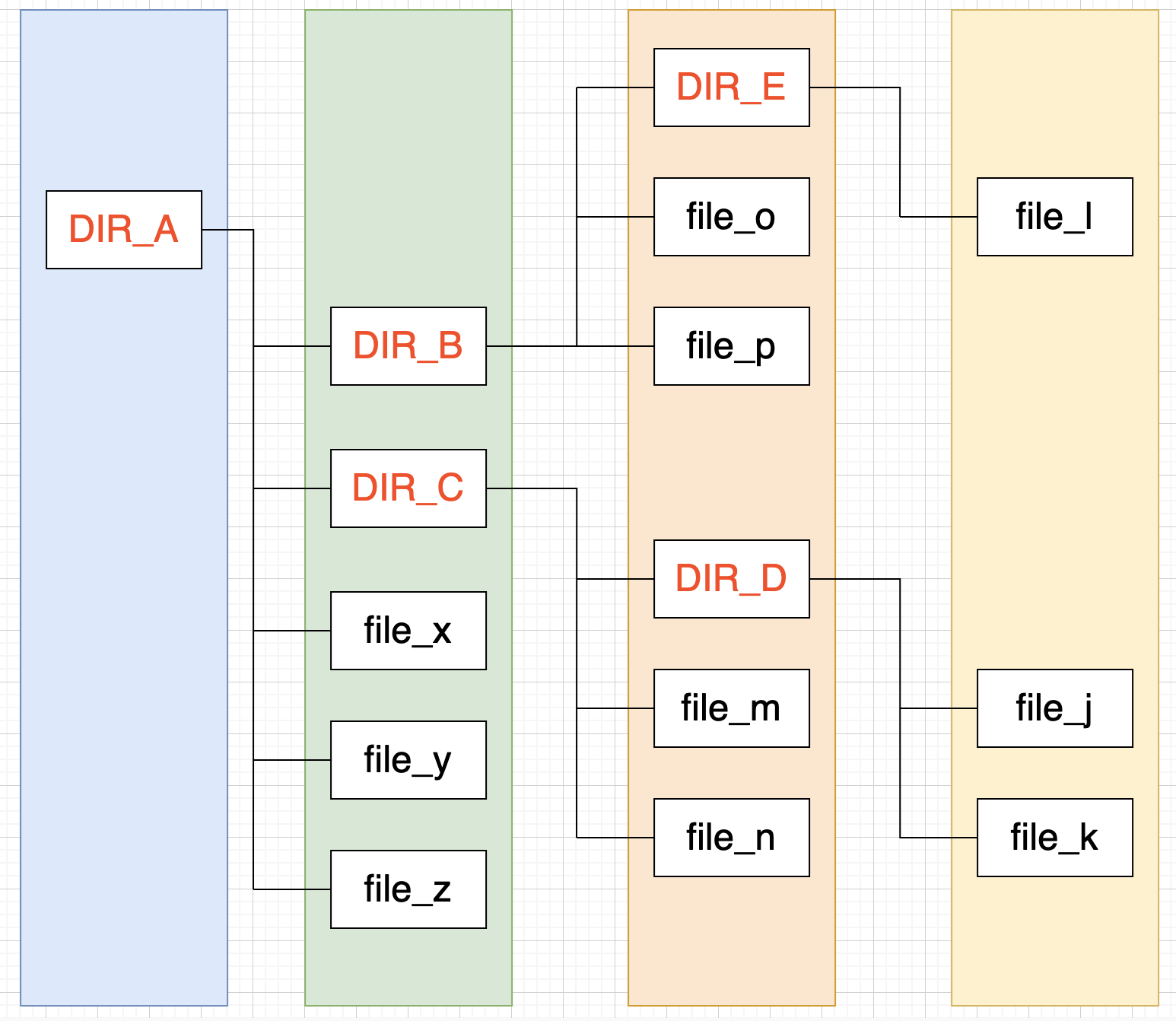
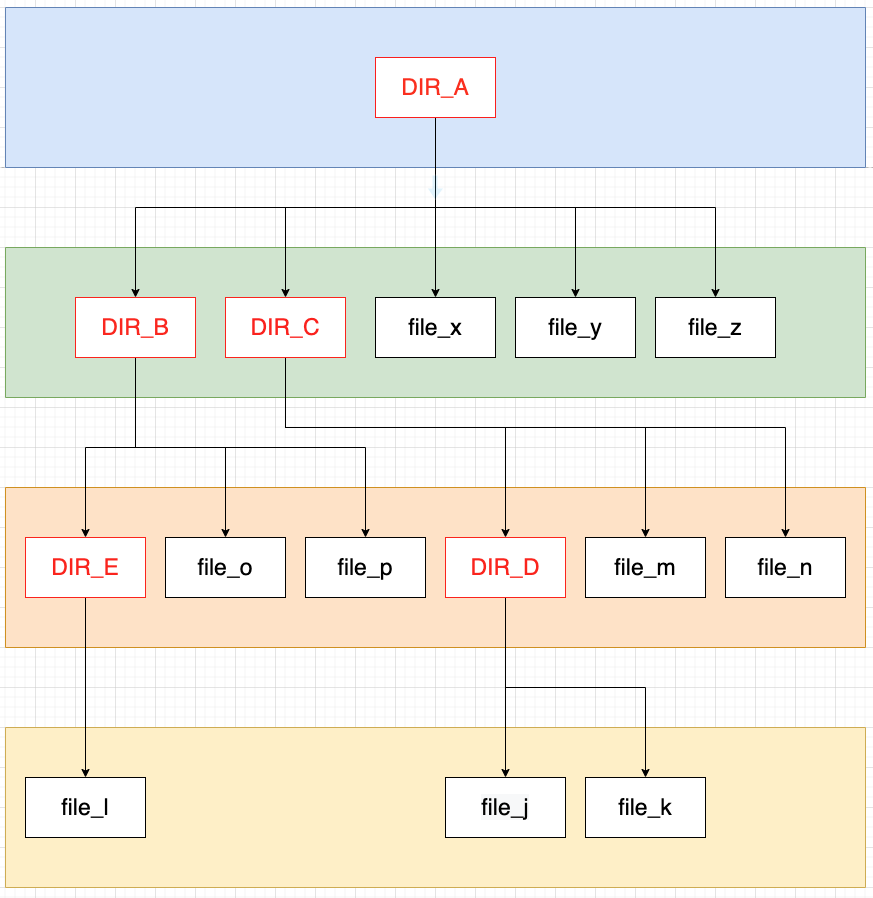
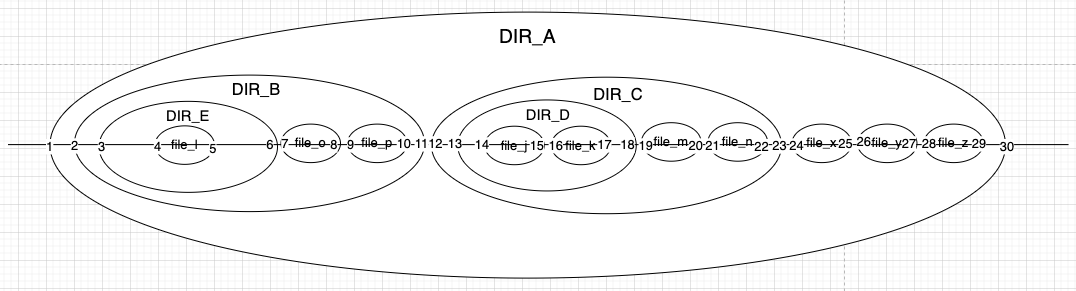
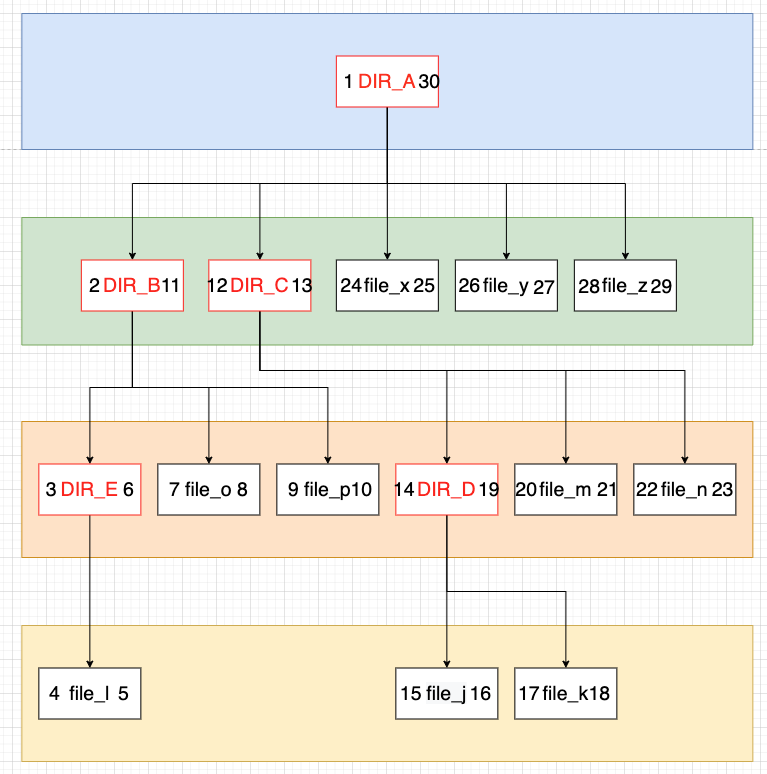
Nested Sets
根据树的深度遍历对节点编号,记录首、末次访问到该节点的数字。通过比较数字或的层级结构关系。
id
name
left
right
1
DIR_A
1
30
2
DIR_B
2
11
3
DIR_C
12
13
4
file_x
24
25
5
file_y
26
27
6
file_z
28
29
7
DIR_E
3
6
8
file_o
7
8
9
file_p
9
10
10
DIR_D
14
19
11
file_m
20
21
12
file_n
22
23
13
file_l
4
5
14
file_j
15
16
15
file_k
17
18
各种情况的处理代价
增
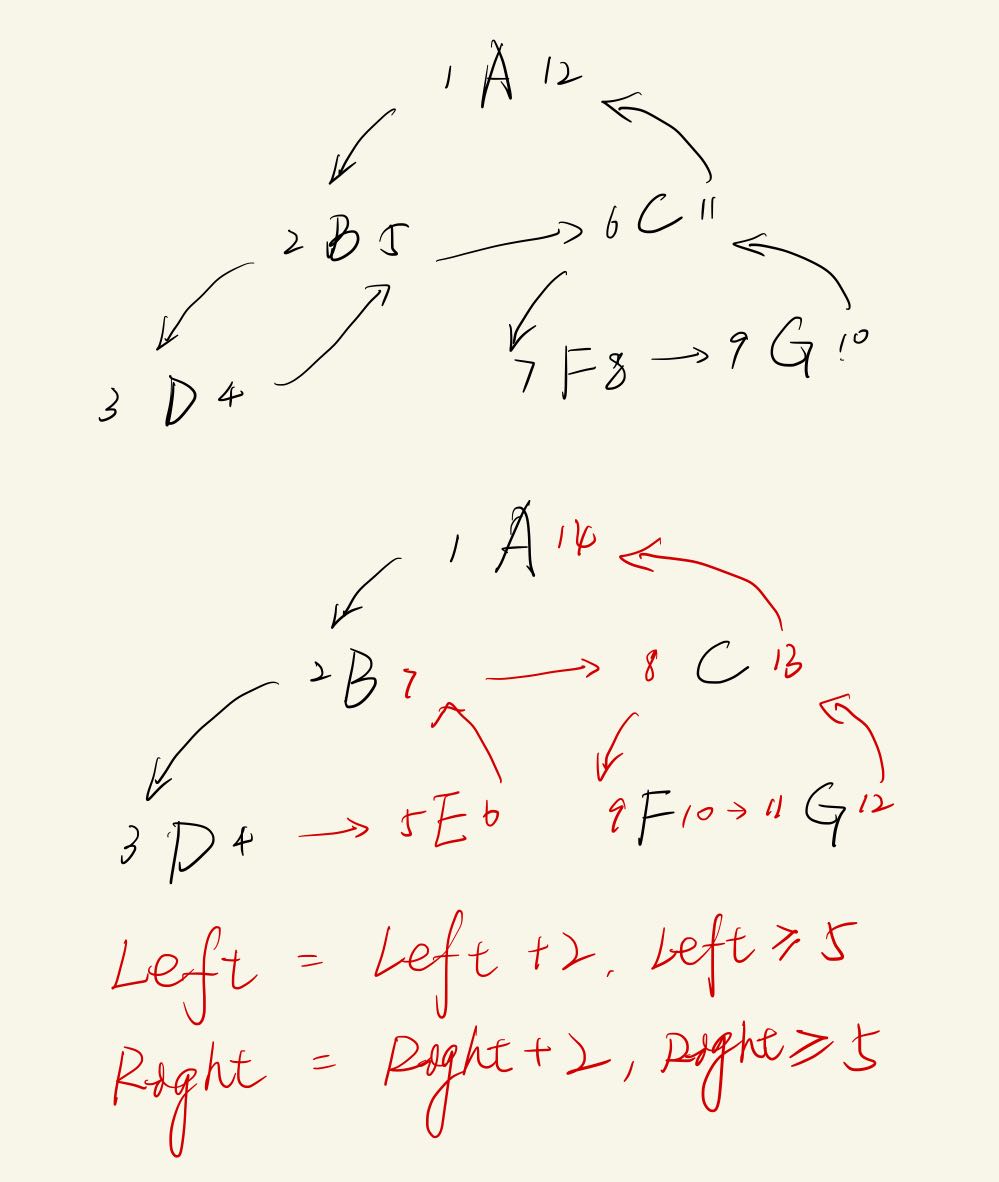
代价:-> O(n),更新会影响到其他子树
parent = $(select * from table where id = $id); insert into table (name, left , right ) values ($name, $parent.right, $parent.right + 1 );update table set left = left + 2 where left >= $parent.right;update table set right = right + 2 where right >= $parent.right;
删
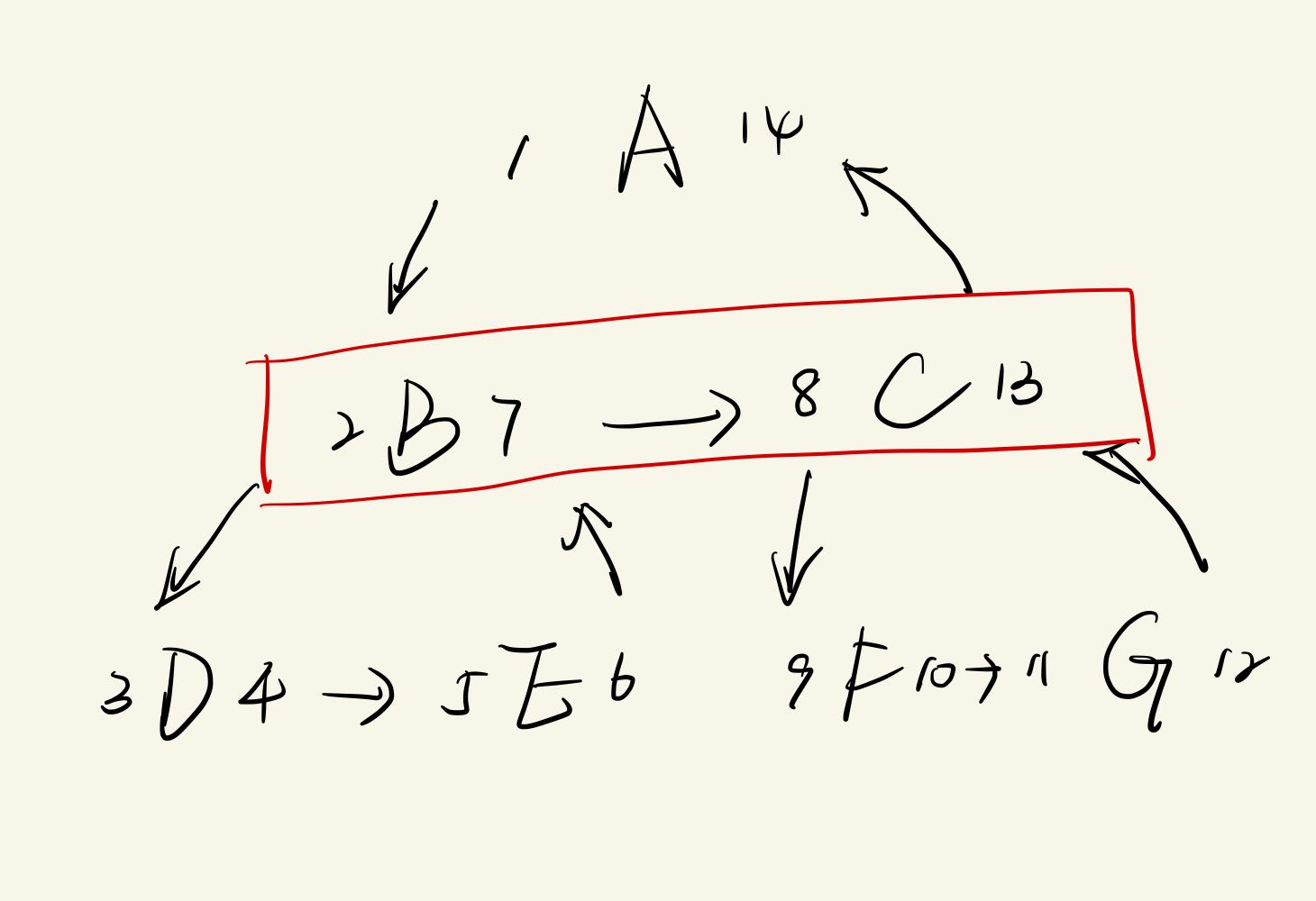
代价:-> O(n),先删除节点以及子树,并对其他子树进行修改
current = $(select * from table where id = $id);delete from table where left >= $current.left and right <= $current.right;d = current.right - current.right + 1 ; update table set left = left - $d where left > $current.right;update table set right = right - $d where right > $current.right;
改
代价:-> O(1)
update table set info where id = $id;
查
查自己
代价:-> O(1)
select * from table where id = $id
查下一级
代价:-> O(n)
select distinct Child.Node, Child.Left, Child.Rightfrom table as child, table as parentwhere parent.left < child.left and parent.right > child.right group by child.node, child.left, child.righthaving max (parent.left) = $parent.left 这类查询可以通过增加一列来简化。例如,增加depth列记录当前节点深度,或者parent_id列记录父节点(和Adjacency List混用),但增加了维护成本
查所有子集
代价:-> O(n)
select * from table where left > $parent.left and right < $parent.right order by left asc ;
移动
代价:-> O(n)
# 先执行 DEL,再执行 ADD current = $( select * from table where id = $id ); # 查询父节点 old_parent = $( select * from table where left < $current.left and right > $current.right order by left desc limit 1 ); node_count = $( select count (* ) from table where left >= $current.left and right <= $current.right ); update table set left = left - node_count* 2 , where left > $current.right;update table set right = right - node_count* 2 where right > $current.right;# 更新子节点 update table set left = left + ($new_parent.right - $current.left), right = right + ($new_parent.right - $current.left) where left >= $current.left and right <= $current.right$current.left = $new_parent.right; $current.right = $new_parent.right + 1 ; update table set left = left + node_count* 2 ,where left > $current.right;update table set right = right + node_count* 2 where right > $current.right;
总结
可以和邻接表同时使用 优点 : 消除递归操作,实现无限分组缺点 : 增 删 改影响范围大适用 : 强要求无限层级深度
比较
T
增
删
改
查自己
查下一级
查所有子集
移动
适用
Adjacency List
O(1)
∞
O(1)
O(1)
O(n)
O(n)
O(1)
不涉及“所有子集”操作,严格按照层级一层层地查询
Closure Table
O(n)
O(n)
O(1)
O(1)
O(n)
O(n)
O(n)
有固定的层级深度,并且层级不多
Path
O(1)
O(n)
O(n)
O(1)
O(n)
O(n)
O(n)
对层级深度有一定限制,并且需求对所有子集进行操作
Netsted Sets
O(n)
O(n)
O(1)
O(1)
O(n)
O(n)
O(n)
强要求无限层级深度